Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMIZ6W2)
| Drug Name |
Norfloxacin
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Baccidal; Barazan; Chibroxin; Fulgram; Lexinor; NFLX; Norflo; Norfloxacine; Norfloxacino; Norfloxacinum; Noroxin; Sebercim; Merck Brand of Norfloxacin; Norfloxacin Merck Brand; AM 0715; AM 715; AM0715; MK 0366; MK 366; MK0366; MK366; AM-0715; AM-715; Chibroxin (TN); Insensye (TN); MK-0366; MK-366; Norflohexal (TN); Norfloxacine [INN-French]; Norfloxacino [INN-Spanish]; Norfloxacinum [INN-Latin]; Norfocin (TN); Noroxin (TN); Nufloxib (TN); Roxin (TN); Utin (TN); Utinor (TN); Apo-Norflox (TN); Norfloxacin (JP15/USP/INN); Norfloxacin [USAN:BAN:INN:JAN]; Chibroxin, MK-366, Baccidal, Sebercim, Zoroxin, Norfloxacin; 1,4-Dihydro-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid; 1-Ethyl-6-fluor-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-chinolincarbonsaeure; 1-Ethyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid; 1-Ethyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-[1-piperazinyl]-3-quinoline-carboxylic acid; 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid; 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-yl-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid; 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-ylquinoline-3-carboxylic acid
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antibiotics
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Enteric bacteria and other eubacteria
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
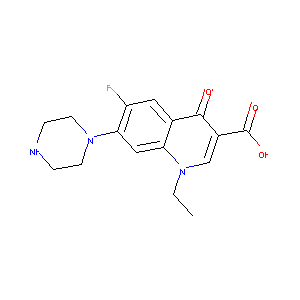 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 319.33 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Norfloxacin
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Norfloxacin (Comorbidity)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | Norfloxacin FDA Label | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2009. Application Number: (ANDA) 074690. | ||||
| 3 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 4 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. | ||||
| 5 | Identification of influx transporter for the quinolone antibacterial agent levofloxacin. Mol Pharm. 2007 Jan-Feb;4(1):85-94. | ||||
| 6 | Breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2) transports fluoroquinolone antibiotics and affects their oral availability, pharmacokinetics, and milk secretion. Drug Metab Dispos. 2006 Apr;34(4):690-5. | ||||
| 7 | Human intestinal transporter database: QSAR modeling and virtual profiling of drug uptake, efflux and interactions. Pharm Res. 2013 Apr;30(4):996-1007. | ||||
| 8 | Clinically significant psychotropic drug-drug interactions in the primary care setting. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2012 Aug;14(4):376-90. | ||||
| 9 | Norfloxacin induces apoptosis and necroptosis in human corneal epithelial cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 2020 Aug;66:104868. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2020.104868. Epub 2020 Apr 19. | ||||
| 10 | Contrasting effects of fluoroquinolone antibiotics on the expression of the collagenases, matrix metalloproteinases (MMP)-1 and -13, in human tendon-derived cells. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005 Dec;44(12):1514-7. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kei087. Epub 2005 Sep 7. | ||||
| 11 | Systems pharmacological analysis of drugs inducing stevens-johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Chem Res Toxicol. 2015 May 18;28(5):927-34. doi: 10.1021/tx5005248. Epub 2015 Apr 3. | ||||
| 12 | Computational and experimental studies on the inhibitory mechanism of hydroxychloroquine on hERG. Toxicology. 2021 Jun 30;458:152822. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2021.152822. Epub 2021 May 28. | ||||
| 13 | Ball P "Quinolone-induced QT interval prolongation: a not-so-unexpected class effect." J Antimicrob Chemother 45 (2000): 557-9. [PMID: 10797074] | ||||
| 14 | Product Information. Fycompa (perampanel). Eisai Inc, Teaneck, NJ. | ||||
| 15 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 16 | Product Information. Xospata (gilteritinib). Astellas Pharma US, Inc, Deerfield, IL. | ||||
| 17 | Owens RC "Risk assessment for antimicrobial agent-induced QTc interval prolongation and torsades de pointes." Pharmacotherapy 21 (2001): 301-19. [PMID: 11253855] | ||||
| 18 | Product Information. Sirturo (bedaquiline). Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Titusville, NJ. | ||||
| 19 | Product Information. Arcapta Neohaler (indacaterol). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 20 | Ball P "Ciprofloxacin: an overview of adverse experiences." J Antimicrob Chemother 18 (1986): 187-93. [PMID: 3542945] | ||||
| 21 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 22 | Johnson EJ, MacGowan AP, Potter MN, et al "Reduced absorption of oral ciprofloxacin after chemotherapy for haematological malignancy." J Antimicrob Chemother 25 (1990): 837-42. [PMID: 2373666] | ||||
| 23 | Canadian Pharmacists Association. | ||||
| 24 | Product Information. Daurismo (glasdegib). Pfizer U.S. Pharmaceuticals Group, New York, NY. | ||||
| 25 | Bengtsson B, Fagerstrom PO "Extrapulmonary effects of terbutaline during prolonged administration." Clin Pharmacol Ther 31 (1982): 726-32. [PMID: 7042176] | ||||
| 26 | Friedman CI, Huneke AL, Kim MH, Powell J "The effect of ampicillin on oral contraceptive effectiveness." Obstet Gynecol 55 (1980): 33-7. [PMID: 7188714] | ||||
| 27 | Davis RL, Kelly HW, Quenzer RW, Standefer J, Steinberg B, Gallegos J "Effect of norfloxacin on theophyllin metabolism." Antimicrob Agents Chemother 33 (1989): 212-4. [PMID: 2719466] | ||||
| 28 | Product Information. Austedo (deutetrabenazine). Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, North Wales, PA. | ||||
| 29 | Product Information. Ingrezza (valbenazine). Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc., San Diego, CA. | ||||
| 30 | Product Information. Rukobia (fostemsavir). ViiV Healthcare, Research Triangle Park, NC. | ||||
| 31 | Anson BD, Weaver JG, Ackerman MJ, et al. "Blockade of HERG channels by HIV protease inhibitors." Lancet 365 (2005): 682-686. [PMID: 15721475] | ||||
| 32 | Product Information. Nexletol (bempedoic acid). Esperion Therapeutics, Ann Arbor, MI. | ||||
| 33 | Product Information. Hetlioz (tasimelteon). Vanda Pharmaceuticals Inc, Rockville, MD. | ||||
| 34 | Nix DE, Wilton JH, Ronald B, Distlerath L, Williams VC, Norman A "Inhibition of norfloxacin absorption by antacids." Antimicrob Agents Chemother 34 (1990): 432-5. [PMID: 2334155] | ||||
| 35 | Product Information. Xalkori (crizotinib). Pfizer U.S. Pharmaceuticals Group, New York, NY. | ||||
| 36 | Product Information. Tagrisso (osimertinib). Astra-Zeneca Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
| 37 | Product Information. Retevmo (selpercatinib). Lilly, Eli and Company, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 38 | Harper KM, Knapp DJ, Criswell HE, Breese GR "Vasopressin and alcohol: A multifaceted relationship." Psychopharmacology (Berl) 235 (2018): 3363-79. [PMID: 32936259] | ||||
| 39 | Ohnishi K, Yoshida H, Shigeno K, et al. "Prolongation of the QT interval and ventricular tachycardia in patients treated with arsenic trioxide for acute promyelocytic leukemia." Ann Intern Med 133 (2000): 881-5. [PMID: 11103058] | ||||
| 40 | Product Information. Braftovi (encorafenib). Array BioPharma Inc., Boulder, CO. | ||||
| 41 | Product Information. Farydak (panobinostat). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 42 | Product Information. Zeposia (ozanimod). Celgene Corporation, Summit, NJ. | ||||
| 43 | FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration "Information for Healthcare Professionals. Fluoroquinolone Antimicrobial Drugs. FDA Alert [7/8/2008].". | ||||
| 44 | Product Information. Wellbutrin XL (buPROPion). GlaxoSmithKline, Philadelphia, PA. | ||||
| 45 | Product Information. Nuplazid (pimavanserin). Accelis Pharma, East Windsor, NJ. | ||||
| 46 | Davey PG "Overview of drug interactions with the quinolones." J Antimicrob Chemother 22(suppl c) (1988): 97-107. [PMID: 3053579] | ||||
| 47 | Product Information. Factive (gemifloxacin). GeneSoft Inc, San Francisco, CA. | ||||
| 48 | Product Information. Barhemsys (amisulpride). Acacia Pharma, Inc, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 49 | Goto M, Sato M, Kitzazawa H, et.al "Papaverine-induced QT interval prolongation and ventricular fibrillation in a patient with a history of drug-induced QT prolongation." Intern Med 53 (2014): 1629-31. [PMID: 25088875] | ||||
| 50 | Ansari SR, Chopra N "Gatifloxacin and Prolonged QT Interval." Am J Med Sci 327 (2004): 55-6. [PMID: 14722399] | ||||
